Tyronib® (Imatinb Mesylate) ⇒ Portfolio
What Tyronib is and what it is used for
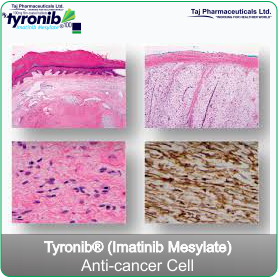
Tyronib is a medicine containing an active substance called imatinib. This medicine works by inhibiting the growth of abnormal cells in the diseases listed below. These include some types of cancer.
Tyronib is a treatment for adults and children for:- Chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML). Leukaemia is a cancer of white blood cells. These white cells usually help the body to fight infection. Chronic myeloid leukaemia is a form of leukaemia in which certain abnormal white cells (named myeloid cells) start growing out of control.
- Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (Ph-positive ALL). Leukaemia is a cancer of white blood cells. These white cells usually help the body to fight infection. Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia is a form of leukaemia in which certain abnormal white cells (named lymphoblasts) start growing out of control. Tyronib inhibits the growth of these cells.
Tyronib is also a treatment for adults for:- Myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative diseases (MDS/MPD). These are a group of blood diseases in which some blood cells start growing out of control. Tyronib inhibits the growth of these cells in a certain subtype of these diseases.
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) and/or chronic eosinophilic leukaemia (CEL). These are blood diseases in which some blood cells (named eosinophils) start growing out of control. Tyronib inhibits the growth of these cells in a certain subtype of these diseases.
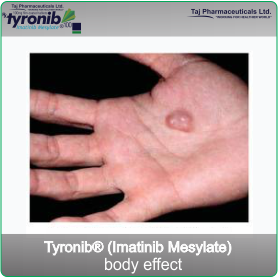
- Gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST). GIST is a cancer of the stomach and bowels. It arises from uncontrolled cell growth of the supporting tissues of these organs.
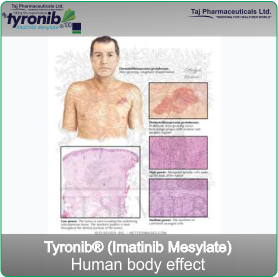
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP). DFSP is a cancer of the tissue beneath the skin in
which some cells start growing out of control. Tyronib inhibits the growth of these cells.
In the rest of this leaflet, we will use the abbreviations when talking about these diseases.
If you have any questions about how Tyronib works or why this medicine has been prescribed for you,
ask your doctor.
What you need to know before you take Tyronib
Tyronib will only be prescribed to you by a doctor with experience in medicines to treat blood cancers or solid tumours.
Do not take Tyronib:- if you are allergic to imatinib or any of the other ingredients of this medicine.
If this applies to you, tell your doctor without taking Tyronib.
If you think you may be allergic but are not sure, ask your doctor for advice.
Talk to your doctor before taking Tyronib:
- if you have or have ever had a liver, kidney or heart problem.
- if you are taking the medicine levothyroxine because your thyroid has been removed.
If any of these apply to you, tell your doctor before taking Tyronib.
Tyronib is also a treatment for children with CML. There is no experience in children with CML below 2 years of age. There is limited experience in children with Ph-positive ALL and very limited experience in children with MDS/MPD, DFSP, GIST and HES/CEL.
Some children and adolescents taking Tyronib may have slower than normal growth. The doctor will monitor the growth at regular visits.
Pregnancy, breast-feeding and fertility ♦ If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby,
ask your doctor for advice before taking this medicine.
♦ Tyronib is not recommended during pregnancy unless clearly necessary as it may harm your
baby. Your doctor will discuss with you the possible risks of taking Tyronib during pregnancy.
♦ Women who might become pregnant are advised to use effective contraception during
treatment.
♦ Do not breast-feed during the treatment with Tyronib.
♦ Patients who are concerned about their fertility while taking Tyronib are advised to consult with
their ask doctor.
How to take Tyronib
Your doctor has prescribed Tyronib because you suffer from a serious condition. Tyronib can help you to
fight this condition. However, always take this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you.
Do not stop taking Tyronib unless your doctor tells you to. If you are not able to take the medicine as
your doctor prescribed or you feel you do not need it anymore, contact your doctor straight away.
Use in adults
Your doctor will tell you exactly how many tablets of Tyronib to take.
♦ If you are being treated for CML:Depending on your condition the usual starting dose is either 400 mg or 600 mg:
♦ 400 mg to be taken as 4 tablets once a day,♦ 600 mg to be taken as 6 tablets once a day.
♦ If you are being treated for GIST:
The starting dose is 400 mg, to be taken as 4 tablets once a day. For CML and GIST, your doctor may prescribe a higher or lower dose depending on how you respond to the treatment. If your daily dose is 800 mg (8 tablets), you should take 4 tablets in the morning and 4 tablets in the evening.
♦ If you are being treated for Ph-positive ALL:The starting dose is 600 mg to be taken as 6 tablets once a day.
♦ If you are being treated for MDS/MPD:The starting dose is 400 mg to be taken as 4 tablets once a day.
♦ If you are being treated for HES/CEL:The starting dose is 100 mg, to be taken as one tablet once a day. Your doctor may decide to increase the dose to 400 mg, to be taken as 4 tablets once a day, depending on how you respond to treatment.
♦ If you are being treated for DFSP:The dose is 800 mg per day (8 tablets), to be taken as 4 tablets in the morning and 4 tablets in the evening.
Use in children and adolescentsThe doctor will tell you how many tablets of Tyronib to give to your child. The amount of Tyronib given will depend on your child’s condition, body weight and height. The total daily dose in children must not exceed 800 mg. The treatment can either be given to your child as a once-daily dose or alternatively the daily dose can be split into two administrations (half in the morning and half in the evening).
When and how to take Tyronib ♦ Take Tyronib with a meal. This will help protect you from stomach problems when taking
Tyronib.
♦ Swallow the tablets whole with a large glass of water.
If you are unable to swallow the tablets, you can dissolve them in a glass of still water or apple juice:
- Use about 50 ml for each 100 mg tablet.
- Stir with a spoon until the tablets have completely dissolved.
- Once the tablet has dissolved, drink everything in the glass straight away. Traces of the dissolved tablets may be left behind in the glass.
Keep taking Tyronib every day for as long as your doctor tells you.
If you take more Tyronib than you shouldIf you have accidentally taken too many tablets, talk to your doctor straight away. You may require medical attention. Take the medicine pack with you.
If you forget to take Tyronib ♦ If you forget a dose, take it as soon as you remember. However if it is nearly time for the next
dose, skip the missed dose.
♦ Then continue with your normal schedule.
♦ Do not take a double dose to make up a forgotten dose.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. They are
usually mild to moderate.
These side effects may occur with certain frequencies, which are defined as follows:
- Very common: may affect more than 1 in 10 people.
- Common: may affect up to 1 in 10 people.
- Uncommon: may affect up to 1 in 100 people.
- Rare: may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people.
- Very rare: may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people.
- Not known: frequency cannot be estimated from the available data.
Very common or common side effects:
- Rapid weight gain. Tyronib may cause your body to retain water (severe fluid retention).
- Signs of infection such as fever, severe chills, sore throat or mouth ulcers. Tyronib can reduce the number of white blood cells, so you might get infections more easily.
- Unexpected bleeding or bruising (when you have not hurt yourself).
- Chest pain, irregular heart rhythm (signs of heart problems).
- Cough, having difficulty breathing or painful breathing (signs of lung problems).
- Feeling light-headed, dizzy or fainting (signs of low blood pressure).
- Feeling sick (nausea), with loss of appetite, dark-coloured urine, yellow skin or eyes (signs of liver problems).
- Rash, red skin with blisters on the lips, eyes, skin or mouth, peeling skin, fever, raised red or purple skin patches, itching, burning sensation, pustular eruption (signs of skin problems).
- Severe abdominal pain, blood in your vomit, stools or urine, black stools (signs of gastrointestinal disorders).
- Severely decreased urine output, feeling thirsty (signs of kidney problems).
- Feeling sick (nausea) with diarrhoea and vomiting, abdominal pain or fever (signs of bowel problems).
- Severe headache, weakness or paralysis of limbs or face, difficulty speaking, sudden loss of consciousness (signs of nervous system problems such as bleeding or swelling in skull/brain).
- Pale skin, feeling tired and breathlessness and having dark urine (signs of low levels of red blood cells).
- Eye pain or deterioration in vision.
- Pain in your hips or difficulty walking.
- Numb or cold toes and fingers (signs of Raynaud’s syndrome).
- Sudden swelling and redness of the skin (signs of a skin infection called cellulites).
- Difficulty hearing.
- Muscle weakness and spasms with an abnormal heart rhythm (signs of changes in the amount of potassium in your blood).
- Bruising.
- Stomach pain with feeling sick (nausea).
- Muscle spasms with a fever, red-brown urine, pain or weakness in your muscles (signs of muscle problems).
- Pelvic pain sometimes with nausea and vomiting, with unexpected vaginal bleeding, feeling dizzy or fainting due to low blood pressure (signs of problems with your ovaries or womb).
- Nausea, shortness of breath, irregular heartbeat, clouding of urine, tiredness and/or joint discomfort associated with abnormal laboratory test results (eg. high potassium, uric acid and phosphorous levels and low calcium levels in the blood).
If you get any of the above, tell your doctor straight away.
Other side effects may include:Very common side effects:
- Headache or feeling tired.
- Feeling sick (nausea), being sick (vomiting), diarrhoea or indigestion.
- Rash.
- Muscle cramps or joint, muscle or bone pain.
- Swelling such as round your ankles or puffy eyes.
- Weight gain.
If any of these affects you severely,tell your doctor.
Common side effects:- Anorexia, weight loss or a disturbed sense of taste.
- Feeling dizzy or weak.
- Difficulty in sleeping (insomnia).
- Discharge from the eye with itching, redness and swelling (conjunctivitis), watery eyes or having blurred vision.
- Nose bleeds.
- Pain or swelling in your abdomen, flatulence, heartburn or constipation.
- Itching.
- Unusual hair loss or thinning.
- Numbness of the hands or feet.
- Mouth ulcers.
- Joint pain with swelling.
- Dry mouth, dry skin or dry eye.
- Decreased or increased skin sensitivity.
- Hot flushes, chills or night sweats.
If any of these affects you severely, tell your doctor.
Not known:- Reddening and/or swelling on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet which may be accompanied by tingling sensation and burning pain.
- Slowing of growth in children and adolescents.
If any of these affects you severely, tell your doctor.
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.How to store Tyronib
- Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
- Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton.
- Do not store above 30°C.
- Store in the original package in order to protect from moisture.
- Do not use any pack that is damaged or shows signs of tampering.
- Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
Contents of the pack and other information
What Tyronib contains
- The active substance is imatinib mesilate. Each tablet of Tyronib contains 100 mg imatinib (as mesilate).
- The other ingredients are microcrystalline cellulose, crospovidone, hypromellose, magnesium stearate and anhydrous colloidal silica.
- The tablet coating is made of red iron oxide (E172), yellow iron oxide (E172), macrogol, talc and hypromellose.
Uses
Tyronib® (Imatinb Mesylate), is a targeted therapy used to treat certain types of Leukaemia and soft tissue sarcoma, it may also be used to treat other types of cancers as part of research trial.
Tyronib® (Imatinib Mesylate) may be used to treat:
- Chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML)
- A type of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) called Philadelphia chromosome positive (Ph+ ALL)
- Gastro-intestinal stromal tumours (GISTs)
- A rare type of soft tissue cancer called dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP)
- Other types of cancers as part of a research trial.
Important Safety Information
-
Pregnancy Category D:Imatinib can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There have been post-market reports of spontaneous abortions and infant congenital anomalies from women who have taken Imatinib.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies with Imatinib in pregnant women. Women should be advised not to become pregnant when taking Imatinib. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus. - Nursing Mothers:Imatinib and its active metabolite are excreted into human milk. Based on data from three breastfeeding women taking Imatinib, the milk:plasma ratio is about 0.5 for imatinib and about 0.9 for the active metabolite.
- Pediatric Use:Imatinib safety and efficacy have been demonstrated in children with newly diagnosed Ph+ chronic phase CML and Ph+ ALL. There are no data in children under 1 year of age.
- Geriatric Use: In the CML clinical studies, approximately 20% of patients were older than 65 years. In the study of patients with newly diagnosed CML, 6% of patients were older than 65 years. No difference was observed in the safety profile in patients older than 65 years as compared to younger patients, with the exception of a higher frequency of edema. The efficacy of Imatinib was similar in older and younger patients.
_100mg_logo-header.png)



_100mg_treat.png)